Connections are crucial in pumping systems to keep operations running smoothly improve efficiency and avoid leaks. Flange and threaded connections are commonly used in various pump systems and each offering benefits and uses. When deciding on the connection type, for your pumping systems various categories of connection types should be taken into consideration.
Two of the most widely connections used in pumping system are flanged and threaded, and each type serves a specific purpose depending on the application in which it is being used.
Understanding Pump Connections
Before diving into flanged vs. threaded connections, it’s crucial to understand the importance of connections in pump setups. Connections connect the pump to the piping system enabling transfer. The selection of connection styles can greatly influence system efficiency, maintenance convenience and overall dependability. Whether you opt for robust flange connections or straightforward threaded connections, making an informed choice based on your specific requirements will help you achieve optimal results.
Flange Connections in Pump Systems
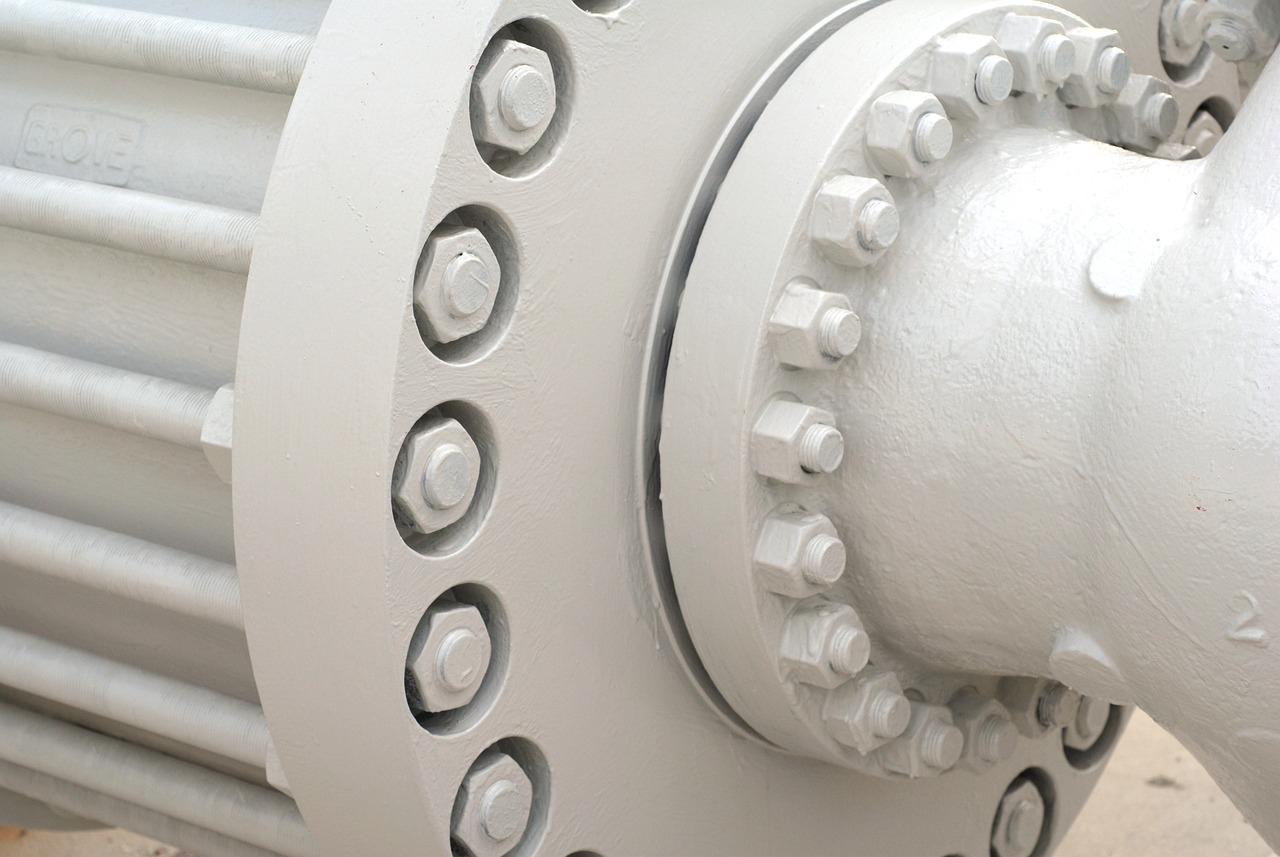
What is a Flange Connection?
A flange connection involves the use of flanges—flat, circular discs with bolt holes—that are bolted together to create a seal. These connections are commonly used in large-diameter pipes and high-pressure applications due to their robustness and ability to provide a tight seal.
Components of a Flange Connection
A typical pump flange connection consists of the following components:
- Flanges: These are the flat discs that connect to the pump and the pipe.
- Gasket: A sealing material placed between the flanges to prevent leaks.
- Bolts and Nuts: Fasteners that secure the flanges together.
Types of Flanges
Flanges come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
- Weld Neck Flanges: Known for their high strength and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature, these flanges are welded to the pipe, providing a smooth transition of fluid flow.
- Slip-On Flanges: These flanges are slipped over the pipe and then welded. They are easier to align and install but are not as strong as weld neck flanges.
- Blind Flanges: Used to close the end of a piping system, these flanges are solid and do not have a bore.
- Socket Weld Flanges: Ideal substitute for small-diameter high-pressure piping, these flanges are welded around the pipe socket, providing a strong connection.
- Threaded Flanges: Similar to slip-on flanges but with internal threads, allowing them to be screwed onto the pipe. They are used in low-pressure systems and can be easily assembled and disassembled.
Advantages of Flange Connections
- Strength and Durability: Flanged connections are robust and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Ease of Maintenance: Flanged connections can be easily disassembled, making it convenient to inspect and maintain the system.
- Leak Prevention: With the right gasket and proper installation, flanged connections provide an excellent seal, minimizing the risk of leaks.
Applications of Flanged Pumps
Flanged pumps are widely used in various industries, including:
- Water Treatment Plants: The robust nature of flanged connections makes them ideal for water pump flange connections in treatment plants, where high pressure and volume are common.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Flanged pumps handle the high pressures and temperatures typical in this industry.
- Chemical Processing: The durability and leak-proof nature of flanged connections make them suitable for handling aggressive chemicals.
Threaded Connections in Pump Systems
What is a Threaded Connection?
Threaded connections involve screwing the pump’s inlet and outlet ports directly into the piping system. These connections are typically used in smaller diameter pipes and low-pressure applications.
Types of Threaded Connections
Threaded connections come in two main types:
- Male Threads: External threads that fit into female threads.
- Female Threads: Internal threads that receive male threads.
Advantages of Threaded Connections
- Ease of Installation: Threaded connections are relatively easy to install and do not require specialized tools or skills.
- Cost-Effective: These connections are typically less expensive than flanged connections, making them a cost-effective option for smaller systems.
- Compact Design: Threaded connections take up less space, making them ideal for compact systems where space is limited.
Disadvantages of Threaded Connections
- Leak Potential: Threaded connections can be prone to leaks if not properly sealed, especially in high-pressure applications.
- Strength Limitations: These connections are not as strong as flanged connections and are best suited for low-pressure applications.
Applications of Threaded Connections
Threaded connections are commonly used in:
- Residential Plumbing: The simplicity and cost-effectiveness of threaded connections make them suitable for residential water systems.
- Small-Scale Industrial Applications: Threaded connections are used in smaller systems where high pressure is not a concern.
- Agricultural Systems: These connections are ideal for irrigation systems and other agricultural applications where ease of installation and maintenance is crucial.
Choosing Between Flange and Threaded Connections
Factors to Consider
When deciding between flange and threaded connections, several factors should be considered:
- Pressure and Temperature: Flanged connections are better suited for high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to their strength and durability.
- Size of the System: Threaded connections are ideal for smaller systems with low pressure, while flanged connections are more suitable for larger systems.
- Ease of Maintenance: Flanged connections are easier to disassemble and maintain, making them a better choice for systems that require frequent maintenance.
- Cost: Threaded connections are generally less, making them a more cost-effective option for small-scale systems.
Best Practices for Installation
Regardless of the connection type, proper installation is crucial to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the pump system:
- Ensure Proper Alignment: Misalignment can cause stress on the connections and lead to leaks or failures.
- Use Quality Gaskets and Seals: For flanged connections, use high-quality gaskets that match the application requirements to prevent leaks.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the pump and piping system manufacturer’s guidelines for “best installation practices.”
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the connections for signs of wear, leaks, or other issues to address potential problems before they become significant.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are key to extending the lifespan of your pump system and ensuring optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips for Flanged Connections
- Regular Bolt Tightening: Check and tighten the bolts regularly to ensure the flanges remain securely connected.
- Gasket Inspection: Inspect the gaskets for signs of wear or damage and replace them as needed to maintain a proper seal.
- Alignment Checks: Regularly check the alignment of the flanges to prevent stress on the connection and ensure smooth operation.
Maintenance Tips for Threaded Connections
- Sealant Application: Apply thread sealant or tape to the threads during installation to prevent leaks.
- Regular Inspection: Inspect the threaded connections regularly for signs of leaks or damage.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Over-tightening threaded connections can damage the threads and lead to leaks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Leaks: Leaks can occur due to improper installation, worn gaskets, or damaged threads. Inspect the connections and replace any damaged components.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration can cause stress on the connections, leading to leaks or failures. Ensure proper alignment and use vibration dampening measures.
- Corrosion: Corrosion can weaken the connections over time. Inspect the connections regularly and address any signs of corrosion promptly.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of flange and threaded connections in pump systems is essential for selecting the right connection type, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining the system’s performance. While flanged connections offer strength, durability, and ease of maintenance for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, threaded connections provide a cost-effective and straightforward solution for smaller, low-pressure systems.


Get Social